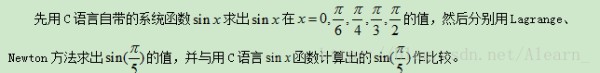
【说明】插值与拟合
在科学研究和工程中,许多问题都可以用y = f(x)来表示其某种内在规律的数量关系,不仅函数f(x)是各种各样的,而且有的函数很复杂,甚至没有明显的解析表达式
因此可以采用两种方法:插值法和拟合法,来求一个近似解。
其中插值法主要思想是 取n个点 pi = yi,然后找到一个简单函数p(x)近似f(x),使得p(xi) = f(xi);
而拟合法主要的思想是 |pi - yi| < exp;从而构造p(x)近似f(x)
【数学理论依据】
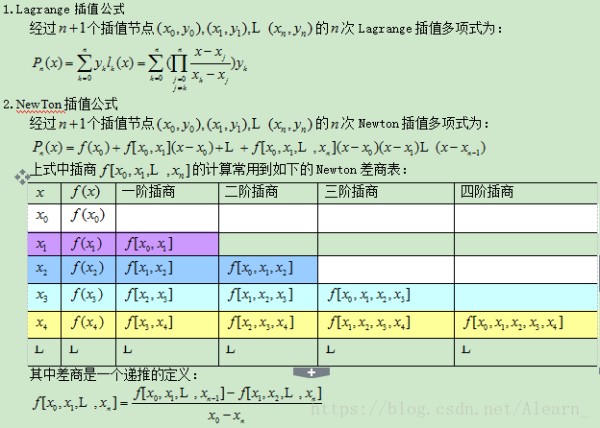
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> #include <string.h> #define N 5 #define pi 3.1415926 /********************************************* *求解差值多项式1.lagrange差值法 * 2.newton差值法 * *x 0 pi/6 pi/4 pi/3 pi/2 *y 0 0.5 0.707104 0.866025 1 *******************************************/ typedef struct { double x; double y; }ADT; /************************************************ *拉格朗日插值法 * ************************************************/ double Lagrange(double temp, ADT *point) { double result = 0; int i = 0,j = 0; double t; for (i = 0; i < N; i++) { t = 1; for (j = 0; j < N; j++) { if (i != j) { t *= (temp - point[j].x) / (point[i].x - point[j].x); } } result += t * point[i].y; } return result; } /******************************************************** *牛顿插值法 * 优点: * 利用一个滚动数组来保存值,减少存储空间 *********************************************************/ void show(ADT *p) { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { printf("%10lf -- %10lf\n",p[i].x, p[i].y); } printf("over\n"); } double Newton(double temp, ADT *point) { double ans = point[0].y; int i = 0, j = 0; double t = 1; //求解系 for (i = 1; i < N; i++) { show(point); t *= (temp - point[i-1].x); printf("t = %lf \n",t); for (j = 0; j < N - i; j++) { printf("(%10lf -%10lf) / (%10lf -%10lf) \n", point[j + 1].y,point[j].y, point[i + j].x,point[j].x ); //每次计算对角线结果均保存在point[0].y中 point[j].y = (point[j + 1].y - point[j].y) / (point[i + j].x - point[j].x) ; } ans += (point[0].y * t); } return ans; } int main() { double temp = pi / 5; // int i,j; double result; printf("调用库函数的ans%4lf\n",sin(temp)); //定义结构体数据 ADT data[N] = { {0,0}, {pi/6, 0.5}, {pi/4, 0.707104}, {pi/3, 0.866025}, {pi/2,1 } }; //调用函数 // result = Lagrange(temp, data); // printf("answer = %4lf\n",result); printf("answer = %4lf\n",Newton(temp,data)); return 0; }
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293利用牛顿差值法求解结果



