多元重塑激活内生动力 小城镇旧城更新的永新实践
城市景观规划是城市更新和城市形象塑造的重要手段。 #生活乐趣# #生活艺术# #城市生活艺术# #城市景观规划#
摘要:
目的
梳理中国旧城更新的发展脉络,大城市已经产生许多成功的案例,然而小城镇的旧城更新面临着更新定位不清、缺乏资金来源、更新主体不明确、历史文化资源状况不佳的困境。
方法
以江西省永新县旧城更新为例,采用多元主体参与的方式,通过建筑更新、街道更新、公共空间设置、滨水绿地建设等措施,在尽可能保持原状建筑和城市肌理的情况下植入新的功能与空间。
结果
实践一方面解决了破、危房带来的安全与风貌问题,另一方面以低造价、实用性的更新原则提升了老城的物质环境,保存了古城的历史文化并且满足于当代的生活需求,延续了场所精神,促进了文化的复兴与经济的发展。
结论
永新实践为当代中国小城镇旧城更新提供了参考与启示。
Abstract:
Objective
At present, the practice of urban renewal in China’s large cities is in the ascendant, and many successful cases have been produced. However, much less attention has been paid to urban renewal in small towns, and there are few successful practical cases in this regard. With their historical and cultural values being neglected, small towns currently faces a lot of problems such as population loss, dilapidated old city space, and slow economic development, making them no longer suitable for modern urban life in many aspects. Although in urgent need of renewal, small towns lack the motivation and standards for renewal.
Methods
The old city renewal project of Yongxin County adopts a multi-party collaborative approach. In the early stage of the project, the cooperation team carried out detailed planning, and selected the southern area of the old city centered on Xingfu Street, Minzhu Street and Shengjiaping Road to explore renewal strategy and method. The “Yongxin Model” uses the power of multiple subjects to carry out small-scale organic renewal in combination with government funds and social capital. In order to maintain the pattern of old streets and the living atmosphere of the old city, all the existing buildings are retained in the renewal practice of Yongxin old city, and the interface of street space is improved by micro-renovation, providing more possibilities for functional intervention and spontaneous renewal of buildings along the street. On the basis of maintaining the characteristics of the original streets and alleys, the renewal plan optimizes the infrastructure and ground texture of streets. The landscape team builds several small-scale pocket gardens using the open spaces along the street formed by the collapse of building. The landscape team also uses the height difference between the existing embankment and the city to place the planned municipal road below the flood embankment, forming a wide riverside belt garden and waterfront walkway above the road.
Results
The renewal plan respects the buildings, spaces and lifestyle left over from the old city, and introduces new functions and spaces while maintaining the texture and original state of the old city as much as possible. On the one hand, the renewal plan solves the safety and style problems brought about by dilapidated houses; on the other hand, it preserves the history and culture of Yongxin old city old and implants that into contemporary life. Yongxin old city renewal neither demolishes any building nor destroys the original facade materials of buildings, but adds modular combination elements to each building. These elements not only beautify the facade of buildings, but also take into account the practicality, effectively improving the style and quality of buildings. The renovated and newly built buildings maintain the pattern of the old city, and pipeline burying and laying and street boundary renovation make the old streets look clean and beautiful. The newly built pocket gardens not only meet the needs of residents along the streets, but also attract surrounding residents, becoming the most dynamic place in the old city. Rather than displacing the residents in the old city, the renewal plan improves the living conditions of these residents and meets their new needs, while maintaining their lifestyle and preserving the hustle and bustle of the old city. The organic integration of new and old buildings successfully continues the traditional culture of Yongxin, while bringing a new look to it, which not only helps Yongxin regain its own cultural context, but also further strengthens the cultural characteristics of Yongxin’s blocks through diverse elements, thus realizing the revival of culture. The improvement of the overall environment of Yongxin old city plays a significant role in attracting investment and promoting population return, which, coupled with subsequent planning and operation and implantation of various cultural activities, has greatly improved the commercial value of Yongxin old city.
Conclusion
Yongxin old city renewal explores a way to promote the comprehensive development of old urban areas of small towns. There will still be a large number of urban renewal actions in China in the future. Yongxin’s research and practice may provide useful reference and inspiration for old city renewal of small towns in China.
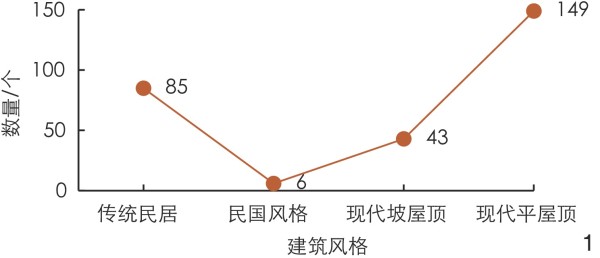
图 1 沿街建筑风格及数量
Figure 1. Architectural styles and quantity of buildings along the streets
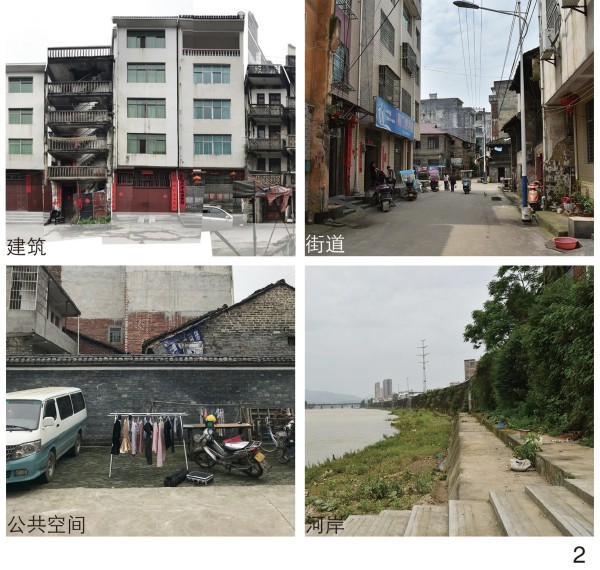

图 2 永新旧城现状
Figure 2. Current states of Yongxin old city
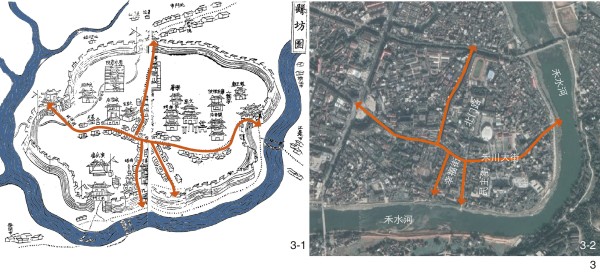
图 3 永新保留的街道肌理[32]
Figure 3. Street texture preserved in Yongxin[32]
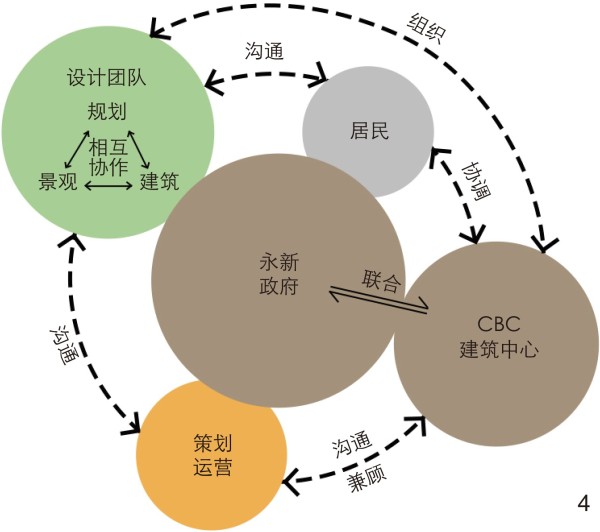
图 4 永新旧城更新模式
Figure 4. Renewal mode of Yongxin old city
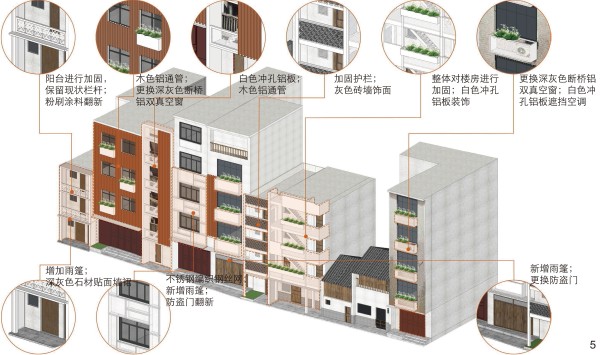
图 5 幸福街部分现代风貌建筑立面改造措施
Figure 5. Facade renovation of some modern buildings along Xingfu Street
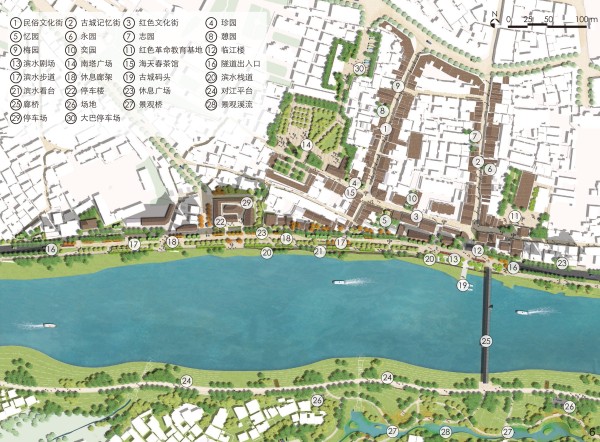
图 6 永新旧城景观设计总平面图
Figure 6. Master plan of landscape design of Yongxin old city
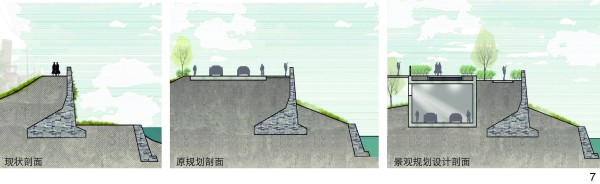
图 7 滨江绿地剖面示意图
Figure 7. Sectional diagram of riverside green space

图 8 现代风貌建筑改造效果
Figure 8. Renovation effects of modern buildings

图 9 整洁有序的街道
Figure 9. Neat and orderly street

图 10 口袋花园
Figure 10. Pocket garden

图 11 当地居民自发在广场上举行活动
Figure 11. Local residents spontaneously hold activities in the square

图 12 咖啡店创业者在门口弹唱
Figure 12. Coffee shop entrepreneurs play and sing at the door

图 13 艺术家在南塔下布置花艺艺术展
Figure 13. Artists arrange a floral art exhibition under the South Tower
[1] 陶希东.城市更新:一个基础理论体系的尝试性构建[J].创新,2017,11(4):16-26.TAO X D. Urban Renewal: An Attempt to Construct Basic Theoretical System[J]. Innovation,2017,11 (4): 16-26.
[2] 刘伯霞,刘杰,程婷,等.中国城市更新的理论与实践[J].中国名城,2021,35(7):1-10.LIU B X,LIU J,CHENG T,et al. The Theory and Practice of Urban Renewal in China[J]. China Ancient City,2021,35 (7): 1-10.
[3] 邹兵.增量规划向存量规划转型:理论解析与实践应对[J].城市规划学刊,2015(5):12-19.ZOU B. The Transformation from Greenfield-Based Planning to Redevelopment Planning: Theoretical Analysis and Practical Strategies[J]. Urban Planning Forum,2015 (5): 12-19.
[4] 王晖.城市的非正规性:我国旧城更新研究中的盲点[J].华中建筑,2008(3):152-155.WANG H. Nonnormal City: Neglected Problem in the Study of Chinese Urban Renovation[J]. Huazhong Architecture,2008 (3): 152-155.
[5] 顾朝林.城市群研究进展与展望[J].地理研究,2011,30(5):771-784.GU C L. Study on Urban Agglomeration: Progress and Prospects[J]. Geographical Research,2011,30 (5): 771-784.
[6] 佘高红,吕斌.转型期小城市旧城可持续再生的思考[J].城市规划,2008(2):16-21.SHE G H,LYU B. Thoughts over Sustainable Urban Regeneration of Small Cities in Transitional Period[J]. City Planning Review,2008 (2): 16-21.
[7] 陈易.转型期中国城市更新的空间治理研究: 机制与模式[D].南京: 南京大学, 2016.CHEN Y. Study on Spatial Governance of Urban Renewal in China Transformation Period: Mechanism and Model[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2016.
[8] 单霁翔.从“大拆大建式旧城改造”到“历史城区整体保护”:探讨历史城区保护的科学途径与有机秩序(中)[J].文物,2006(6):36-48.SHAN J X. From “Demolishing and Rebuilding Old City Reconstruction” to “Overall Protection of Historic Urban Areas”: To Discuss the Scientific Approach and Organic Order of Historical Urban Area Protection (Part 2)[J]. Cultural Relics,2006 (6): 36-48.
[9] 单霁翔.从“大规模危旧房改造”到“循序渐进,有机更新”:探讨历史城区保护的科学途径与有机秩序(下)[J].文物,2006(7):26-40.SHAN J X. From “Large-Scale Dilapidated Housing Renovation” to “Step-by-Step,Organic Renewal”: To Discuss the Scientific Approach and Organic Order of the Protection of Historical Urban Areas (Part 3)[J]. Cultural Relics,2006 (7): 26-40.
[10] 姜文锦,陈可石,马学广.我国旧城改造的空间生产研究:以上海新天地为例[J].城市发展研究,2011,18(10):84-89.JIANG W J,CHENG K S,MA X G. Study on the Spatial Production of Urban Renewal in China: A Case of Shanghai Xintiandi Square[J]. Urban Development Studies,2011,18 (10): 84-89.
[11] 高富丽,王成芳.不同更新模式下的传统商业街更新对比研究:以前门地区两条典型商业街为例[J].住区,2021,4(1):18-26.GAO F L,WANG C F. A Comparative Study on the Renewal of Traditional Commercial Streets Under Different Renewal Modes: Take Two Typical Commercial Streets in Qianmen District as an Example[J]. Design Community,2021,4 (1): 18-26.
[12] 王澍.中山路:一条路的复兴与一座城的复兴,杭州,中国[J].世界建筑,2012(5):114-121.WANG S. Zhongshan Road: Renovation of a Road and a City,Hangzhou,China,2009[J]. World Architecture,2012 (5): 114-121.
[13] 谭俊杰,常江,谢涤湘.广州市恩宁路永庆坊微改造探索[J].规划师,2018,34(8):62-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2018.08.010TAN J J,CHANG J,XIE D X. Micro Renovation of Yongqing Block,Enning Road,Guangzhou[J]. Planners,2018,34 (8): 62-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2018.08.010
[14] 刘垚,田银生,周可斌.从一元决策到多元参与:广州恩宁路旧城更新案例研究[J].城市规划,2015,39(8):101-111.LIU Y,TIAN Y S,ZHOU K B. From Unilateral Decision-Making to Multiple Participation in Urban Regeneration: A Case Study on Enning Road Project in Guangzhou[J]. City Planning Review,2015,39 (8): 101-111.
[15] 孟岩,林怡琳,饶恩辰.村/城重生 城市共生下的深圳南头实践[J].时代建筑,2018(3):58-64.MENG Y,LIN Y L,RAO E C. Village/City Coexistence and Regeneration in Nantou,Shenzhen[J]. Time + Architecture,2018 (3): 58-64.
[16] 刘易轩,吕斌.深圳市南头古城城市修补的场所营造路径[J].规划师,2018,34(10):59-65.LIU Y X,LYU B. Place Making in Urban Rehabilitation of Nantou Ancient Town,Shenzhen[J]. Planners,2018,34 (10): 59-65.
[17] 贾蓉.老城复杂系统的集合影响力保护更新实践:以北京西城大栅栏更新计划为例[J].北京规划建设,2019(S2):81-90.JIA R. The Collective Impact and Crossover Revival Practice of the Old City Complex System: Illustrated by the Example of Dashlar Project[J]. Beijing Planning Review,2019 (S2): 81-90.
[18] 阳建强,陈月.1949—2019年中国城市更新的发展与回顾[J].城市规划,2020,44(2):9-19.YANG J Q,CHEN Y. Review on the Development of Urban Regeneration in China from 1949 to 2019[J]. City Planning Review,2020,44 (2): 9-19.
[19] 李云燕,赵万民,朱猛,等.我国新时期旧城更新困境、思路与基本框架思考[J].城市发展研究,2020,27(1):57-66.LI Y Y,ZHAO W M,ZHU M,et al. The Difficulties,Ideas and Basic Framework of Old City Renewal in China in the New Period[J]. Urban Development Studies,2020,27 (1): 57-66.
[20] 陈毅,衷培圆.基于权力、资本和权利三维视角的旧城更新运行机制研究:以历史文化名城苏州为例[J].江淮论坛,2022(1):140-148.CHEN Y,ZHONG P Y. Research on the Operation Mechanism of Old City Renewal Based on the Three-Dimensional Perspective of Power,Capital and Rights: Taking Suzhou,a Famous Historical and Cultural City as an Example[J]. Jianghuai Tribune,2022 (1): 140-148.
[21] 李强,陈宇琳,刘精明.中国城镇化“推进模式”研究[J].中国社会科学,2012(7):82-100.LI Q,CHEN Y L,LIU J M. On the “Development Mode” of Chinese Urbanization[J]. Social Sciences in China,2012 (7): 82-100.
[22] 祝立雄,董文丽,李王鸣.我国城市规划实施评估发展历程、技术特征与演变趋势[J].西部人居环境学刊,2019,34(2):67-73.ZHU L X,DONG W L,LI W M. The Development Process,Technical Characteristics and Evolution Trend of Urban Planning Implementation Evaluation in China[J]. Journal of Human Settlements in West China,2019,34 (2): 67-73.
[23] 李小龙.关中地区县城空间格局的历史营建研究[D].西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2020.LI X L. Research on the Historical Planning and Construction Genes of Urban Spatial Pattern in Guanzhong Counties[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2020.
[24] 单霁翔.城市文化遗产保护与文化城市建设[J].城市规划,2007(5):9-23.SHAN J X. Urban Cultural Heritage Protection and Cultural City Construction[J]. City Planning Review,2007 (5): 9-23.
[25] 胡蓉.中小型城市特色产业发展研究[D].重庆: 重庆大学, 2011.HU R. Researching the Characteristics of Industrial Development of Small and Medium-Sized[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2011.
[26] 左妮莎,邹一挥.中小城市传统商业街治理结构问题及规划应对[J].小城镇建设,2015,4(8):80-87.ZUO N S,ZOU Y H. Governance Structure Problems and Planning Solutions of Traditional Commercial Streets in Small and Medium-Sized Cities[J]. Development of Small Cities & Towns,2015,4 (8): 80-87.
[27] 焦红,贾丽丽.新型城镇化视角下小城镇规划的慢城模式探索[J].学术交流,2016(12):123-128.JIAO H,JIA L L. Exploration of the Slow City Mode of Small Town Planning from the Perspective of New Urbanization[J]. Academic Exchange,2016 (12): 123-128.
[28] 阳建强.走向持续的城市更新:基于价值取向与复杂系统的理性思考[J].城市规划,2018,42(6):68-78.YANG J Q. Towards Sustainable Urban Regeneration: Based on the Rational Thinking of Value Orientation and Complex System[J]. City Planning Review,2018,42 (6): 68-78.
[29] 容志,张云翔.社区微更新中政社共同生产的类型与生成逻辑:基于上海市Y社区的实践案例分析[J].探索,2020(3):127-141.RONG Z,ZHANG Y X. Types and Practice Logic of Co-production Between Government and Community During the Community Micro-regeneration: Based on a Case Study of Y Community in Shanghai[J]. Probe,2020 (3): 127-141.
[30] 林岩.以环境和需求为导向的小城镇“自下而上”城市设计途径研究[D].南京: 东南大学, 2019.LIN Y. Research on “Bottom-Up” Urban Design Approaches of Small Towns Oriented by environment and Demands[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2019.
[31] 王颖.历史街区保护更新实施状况的研究与评价[D].南京: 东南大学, 2015.WANG Y. The Research and Evaluation for Current Protections and Developments in Historical Urban Area[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015.
[32] 《永新县志》编委会.永新县志[M].北京: 新华出版社, 1992.Editorial Committee of Yong Xin Xian Zhi. Yong Xin Xian Zhi [M]. Beijing: Xinhua Publishing House,1992.
[33] 陈晓虹.日常生活视角下旧城复兴设计策略研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2014.CHEN X H. Research of Old City Regeneration Design Strategy Based on Everyday Life[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2014.
[34] 国务院办公厅.住房和城乡建设部关于在实施城市更新行动中防止大拆大建问题的通知[EB/OL].(2021-08-30)[2022-08-31].http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-08/31/content_5634560.htm.Office of the State Council. Notice of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development on Preventing Large-Scale Demolition and Construction in the Implementation of Urban Renewal Actions[EB/OL]. (2021-08-30)[2022-08-31]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-08/31/content_5634560.htm.
网址:多元重塑激活内生动力 小城镇旧城更新的永新实践 https://www.yuejiaxmz.com/news/view/558019
相关内容
上城区3个项目入选城镇老旧小区改造实践典范案例边兰春:城市更新不仅要升级物质空间,还要重塑生活方式
江苏无锡:城市更新,生活向“新”!
城市更新的当涂实践:向绿而生,打造宜居滨江花园城市
中经评论:城镇老旧小区持续“焕新”,幸福生活不断“扩容”
城市更新与老旧小区改造:中国城市的蝶变之路
旧物重生——公共艺术激活城市空间的探索研究
城市“微更新”让更多小确幸点亮生活
城市更新,让生活更美好(共建共享“高品质生活”⑤)
【新时代文明实践】城郊镇:倡导移风易俗 弘扬婚育新风

