基于深度学习FasterRCNN模型Restnet50 的生活垃圾智能分类(准确率达84%)
学习并掌握正确的垃圾分类知识,提高生活垃圾分类效率。 #生活技巧# #节省生活成本# #生活垃圾分类指南# #二手物品交易规则#
目录 前言总体设计系统整体结构图系统流程图 运行环境1. 硬件环境2. Python 环境 模块实现1. 数据预处理2. 数据加载3. 模型构建4. 模型训练及保存5. 模型加载与调用 系统测试1. 模型准确率2. 分类别准确率 工程源代码下载其它资料下载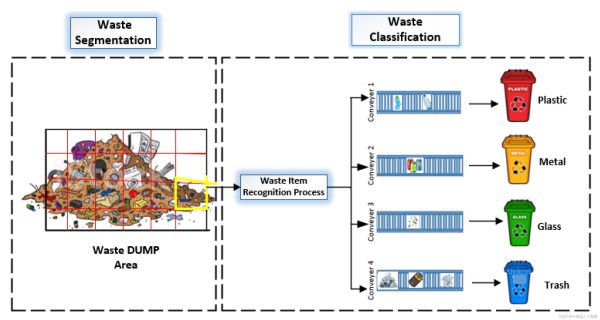
前言
本项目基于Faster R-CNN模型,通过RPN网络(Region Proposal Network)获取图片中的候选区域,并利用RestNet50模型提取特征,旨在实现对生活垃圾的智能分拣。
在该项目中,我们使用Faster R-CNN模型,它是一种经典的目标检测算法,能够同时进行物体检测和区域提议。通过RPN网络,我们能够在输入图片中快速识别出潜在的候选区域,这些区域可能包含生活垃圾物品。
接下来,我们使用RestNet50模型进行特征提取。RestNet50是一种深度卷积神经网络,具有较强的特征提取能力。我们将候选区域输入RestNet50模型,提取出高维特征表示,以捕捉垃圾物品的关键信息。
通过将候选区域和其对应的特征输入到后续的分类器中,我们可以对生活垃圾进行智能分拣。分类器可以根据特征表示判断每个候选区域属于哪一类垃圾,例如可回收物、厨余垃圾、有害垃圾等,实现智能化的垃圾分类过程。
本项目的目标是利用Faster R-CNN模型和RestNet50模型的结合,通过智能化的图片分析和特征提取,实现对生活垃圾的智慧分拣。这项技术有助于提高垃圾处理的效率和准确性,为环境保护和资源回收做出贡献。
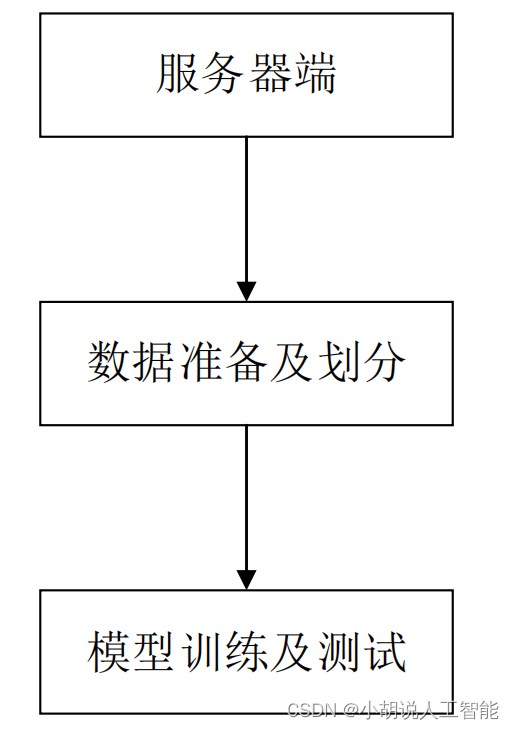
总体设计
本部分包括系统整体结构图和系统流程图。
系统整体结构图
系统整体结构如图所示。
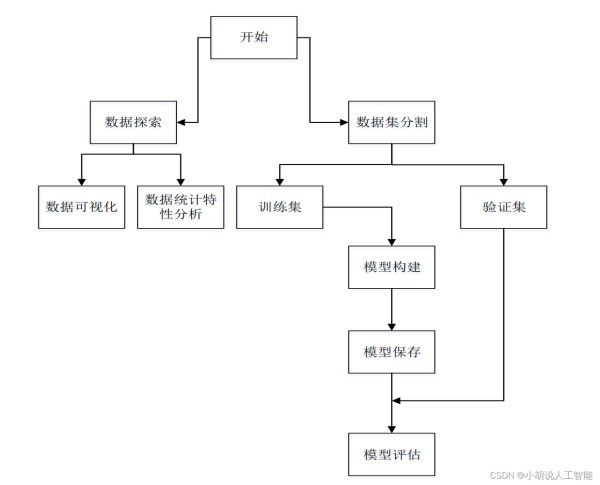
系统流程图
系统流程如图所示。
运行环境
本部分包括硬件环境和 Python 环境。
1. 硬件环境
FasterRCNN 对计算要求较高,有一部分是 Restnet50 的卷积层。必须使用较大内存的GPU 才可以完成训练。在本项目中,用华为云提供的模型训练服务(GPU tesla P100)实现,链接:https://www.hwtelcloud.com/products/mts。
2. Python 环境
使用软件的主要版本如下:
Python==3.6
TensorFlow==1.13.1
Keras==2.0.3
CV2
naie(是华为针对器模型训练服务所设计的库)
模块实现
本项目包括 5 个模块:数据预处理、数据加载、模型构建、模型保存及训练、模型加载及调用,下面分别给出各模块的功能介绍及相关代码。
1. 数据预处理
数据下载地址: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ZAbzYMLv0fcLFJsu64u0iw,提取码:yba3
数据信息被存储在 json 文件中,使用 python 和 jupyter notebook 对 json 文件进行解析,并进行数据探索。经过分析,获取的垃圾数据集中单类垃圾共有 80000 张训练集图片,204种分类。且每种分类的垃圾图片数量基本相同,约为 300 张左右。由于时间短,仅使用了10种类别的单类图片用于训练和验证,这 10 种类别分别是瓜子壳、核桃、花生壳、面包、饼干、菌菇类、菜叶、菜根、甘蔗皮、中药材、枣核。其中训练集有 3000 张,测试集有843张,如图所示。
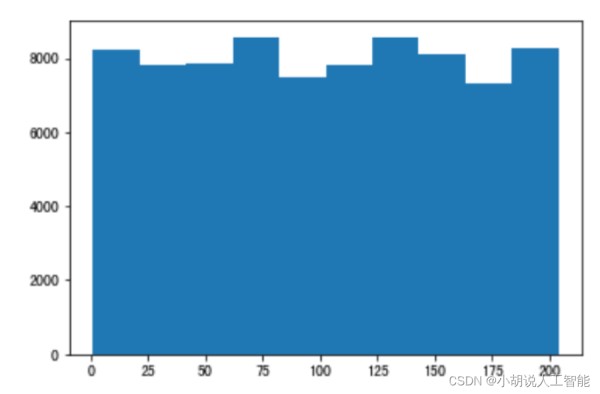
由于 FasterRCNN 使用 anchor 机制,即锚框。需要获取样本尺寸信息作为先验信息,设计锚框。因此,使用 matplotlib 绘制出关于样本尺寸的散点图和直方图。如图1~图 3 所示。
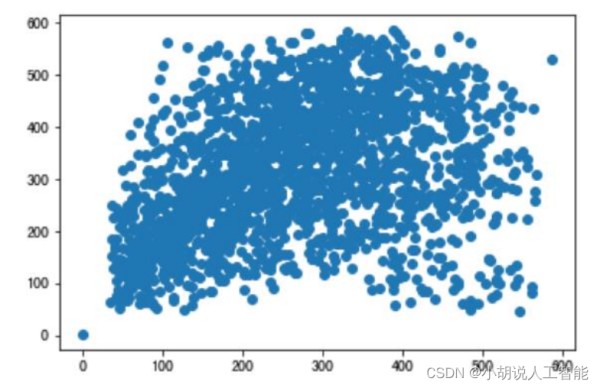
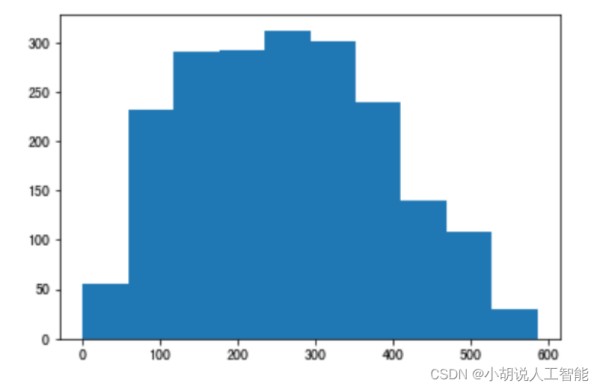
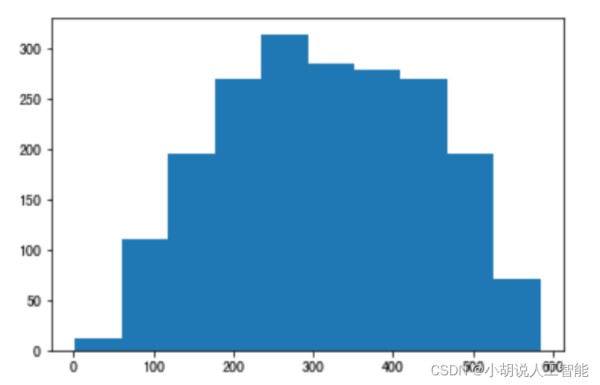
锚框机制,需要预先提供九个不同尺寸的锚框,应尽量贴合目标的尺寸。使用 K-means算法进行聚类,获得合适的锚框,如下图所示。
#使用KMeans确定anchor的长宽 from sklearn.cluster import KMeans from sklearn.externals import joblib data=np.hstack((np.array(widths).reshape((-1,1)),np.array(heights).reshape((-1,1)))) clf = KMeans(n_clusters=9) s = clf.fit(data) centers=clf.cluster_centers_ plt.scatter(widths,heights,alpha=0.2) plt.scatter([i[0] for i in centers ],[i[1] for i in centers ],c='r') 123456789
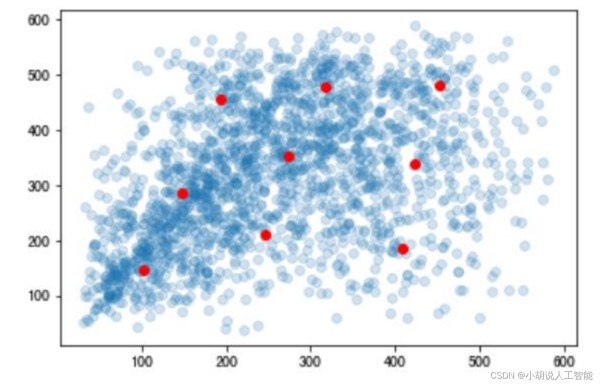
结合Kmeans结果,并进行手动调整,可以设计锚框尺寸。
#锚框尺寸 self.anchor_box_scales = [150, 300, 435] #锚框比例 self.anchor_box_ratios = [[1, 1], [1, 0.91], [1, 1.25]] 1234
2. 数据加载
本项目使用 biendata(https://biendata.com/)的一个比赛,2020 海华 AI 挑战赛垃圾分类。这个比赛,与华为模型训练服务合作,可以直接在华为模型训练平台上下载、读取训练比赛数据。
使用 github 上提供基于 Keras 的 FasterRCNN 模型。该模型需要将图片信息以 VOC2012数据集的格式进行存储,将图片信息转为该格式,代码写在 garbage_dataset.py 中。
def w_voc(self):#将目标的信息写入voc格式数据集中 data_path = 'VOC2012' print("将目标的信息写入voc格式数据集中") #annot_path是存放目标信息xml文件的文件夹 annot_path = os.path.join(data_path, 'Annotations_single') #imgs_path是存放图片的文件夹位置 #imgs_path = os.path.join(data_path, 'JPEGImages') #imgset_path是存放图片名的文件夹 imgsets_path_trainval = os.path.join(data_path, 'ImageSets', 'single', 'trainval.txt') annot_indexs=0#用来标记新图片的起始目标信息位置 if os.listdir(annot_path) != None: os.system('rm -f '+annot_path+'/*') with open(self.json_dir,'r',encoding='utf-8') as fp: self.json_dict = json.load(fp) with open(imgsets_path_trainval,'w') as fp:#将图片名存入imgsets中 for img in self.json_dict['images']: fp.write(img['file_name'].split('/')[1]+'\n') for img in self.json_dict['images']: annots=[] file_name=img['file_name'].split('/')[1] xml_name=file_name.split('.')[0]+'.xml' for annot in self.json_dict['annotations'][annot_indexs:]: #获取每张图片下的目标信息 if str(annot['image_id'])==file_name.split('.')[0]: annots.append(annot) annot_indexs+=1#更新目标信息索引 else: break #将图片信息与目标信息写入xml文件中,并存入annotations文件夹 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829
在 FasterRCNN 中对 VOC 格式数据读取代码存在 keras_frcnn/pascal_voc_parser.py。再通 过 keras_frcnn/data_augment.py 读 取 每 一 张 图 片 信 息 和 相 应 目 标 信 息 ,keras_frcnn/data_generators.py 作为发生器。
3. 模型构建
数据加载进模型之后,需要定义模型结构,并优化损失函数。
1)定义模型结构
从keras_frcnn/resnet.py 调用相关的模型层。
from keras_frcnn import resnet as nn #定义基本网络(此处为Resnet,可以是VGG,Inception等) shared_layers = nn.nn_base(img_input, trainable=True) #定义RPN,建立在基础层上 num_anchors=len(cfg.anchor_box_scales)* len(cfg.anchor_box_ratios) rpn = nn.rpn(shared_layers, num_anchors) classifier = nn.classifier(shared_layers, roi_input, cfg.num_rois,nb_classes=len(classes_count), trainable=True) model_rpn = Model(img_input, rpn[:2]) model_classifier = Model([img_input, roi_input], classifier) #这是一个同时包含RPN和分类器的模型,用于加载/保存模型的权重 model_all = Model([img_input, roi_input], rpn[:2] + classifier) 1234567891011
2. 损失函数及模型优化
#优化器 optimizer = Adam(lr=1e-5) optimizer_classifier = Adam(lr=1e-5) model_rpn.compile(optimizer=optimizer, loss=[losses_fn.rpn_loss_cls(num_anchors),losses_fn.rpn_loss_regr(num_anchors)]) model_classifier.compile(optimizer=optimizer_classifier, loss=[losses_fn.class_loss_cls,losses_fn.class_loss_regr(len(classes_count)-1)], metrics={'dense_class_{}'.format(len(classes_count)):'accuracy'}) model_all.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mae') 123456789
4. 模型训练及保存
本部分包括模型训练和模型保存。
1)模型训练
#相关参数 epoch_length = 1000 num_epochs = int(cfg.num_epochs) iter_num = 0 #调用模型进行训练 X, Y, img_data = next(data_gen_train) loss_rpn = model_rpn.train_on_batch(X, Y) P_rpn = model_rpn.predict_on_batch(X) 12345678
2)模型保存
model_all.save_weights(cfg.model_path) mox.file.copy(cfg.model_path,os.path.join(Context.get_model_path(), 'model_frcnn.vgg.hdf5')) 12
5. 模型加载与调用
Keras 需要先将网络定义好,才能加载模型。相关代码在 test_frcnn_kitti.py 中
1)模型加载
#定义RPN,建立在基础层上num_anchors=len(cfg.anchor_box_scales)*len(cfg.anchor_box_ratios) rpn_layers = nn.rpn(shared_layers, num_anchors) classifier=nn.classifier(feature_map_input,roi_input, cfg.num_rois,nb_classes=len(class_mapping),trainable=True) model_rpn = Model(img_input, rpn_layers) model_classifier_only=Model([feature_map_input,roi_input],classifier) model_classifier= Model([feature_map_input, roi_input], classifier) print('Loading weights from {}'.format(cfg.model_path)) model_rpn.load_weights(cfg.model_path, by_name=True) model_classifier.load_weights(cfg.model_path, by_name=True) model_rpn.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mse') model_classifier.compile(optimizer='sgd', loss='mse') 1234567891011
2)模型测试
def predict_single_image(img_path, model_rpn, model_classifier_only, cfg, class_mapping): #将空间金字塔池应用于建议的区域 boxes = dict() for jk in range(result.shape[0] // cfg.num_rois + 1): rois = np.expand_dims(result[cfg.num_rois * jk:cfg.num_rois * (jk + 1), :], axis=0) if rois.shape[1] == 0: break if jk == result.shape[0] // cfg.num_rois: curr_shape = rois.shape target_shape = (curr_shape[0], cfg.num_rois, curr_shape[2]) rois_padded = np.zeros(target_shape).astype(rois.dtype) rois_padded[:, :curr_shape[1], :] = rois rois_padded[0, curr_shape[1]:, :] = rois[0, 0, :] rois = rois_padded [p_cls, p_regr] = model_classifier_only.predict([F, rois]) for ii in range(p_cls.shape[1]): if np.max(p_cls[0, ii, :]) < bbox_threshold or np.argmax(p_cls[0, ii, :]) == (p_cls.shape[2] - 1): continue cls_num = np.argmax(p_cls[0, ii, :]) if cls_num not in boxes.keys(): boxes[cls_num] = [] (x, y, w, h) = rois[0, ii, :] try: (tx, ty, tw, th) = p_regr[0, ii, 4 * cls_num:4 * (cls_num + 1)] tx /= cfg.classifier_regr_std[0] ty /= cfg.classifier_regr_std[1] tw /= cfg.classifier_regr_std[2] th /= cfg.classifier_regr_std[3] x, y, w, h = roi_helpers.apply_regr(x, y, w, h, tx, ty, tw, th) 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829
系统测试
本部分包括模型准确率和分类别准确率。
1. 模型准确率
通过华为模型训练平台对模型进行测试,并写入result.txt文件中存储,相关代码如下:
true_count=0#使用测试集进行准确度的测试,并存入文件中 with open('./val_single.txt','r') as f: val_data=f.readlines() img_count=len(val_data) for index,val in enumerate(val_data): if index%50 ==0: K.clear_session() test_cls=predict(val.split()[0]) if int(test_cls)==int(val.split()[1]): true_count+=1 with open('/cache/result.txt','a') as f: f.write("%s %s %s\n"%(val.split()[0],val.split()[1],test_cls)) accuray=true_count/img_count with open('/cache/result.txt','a') as f: f.write("val_lenght:%s,accruray:%s"%(img_count,accuray)) 1234567891011121314
数据属性,分别是图片地址,真实标签,识别标签,共有843条数据。以下是部分结果数据,总体准确率为0.840,识别效果比较理想。
/cache/train/images_withoutrect/24726.png 63 63 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/12114.png 3 3 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/24671.png 63 63 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/13764.png 51 51 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/12759.png 19 19 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/11339.png 2 2 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/11451.png 2 2 /cache/train/images_withoutrect/14072.png 50 0 ...... val_lenght:843,accruray:0.8398576512455516 12345678910
2. 分类别准确率
FasterRcnn 模型使用 anchor 机制,anchor 的设置和不同类别识别的准确率息息相关。在这里对分类别准确率进行分析,并计算它们的真实边框和锚点边框的差距。
相关代码如下:
#对结果按类别计算准确度 for category_name in message['categories']: categories_name.append([category_name['id'],category_name['name']]) for category in categorys: print(categories_name[category-1],category) labels=[] categorys_accuray={} with open('result.txt','r') as f: results=f.readlines()[:-1] for result in results: path,true_label,test_label=result.split() true_label=int(true_label) test_label=int(test_label) if true_label not in labels: labels.append(true_label) for label in labels: categorys_img_count=0 categorys_true_count=0 for result in results: path,true_label,test_label=result.split() true_label=int(true_label) test_label=int(test_label) if true_label==label: categorys_img_count+=1 if true_label==test_label: categorys_true_count+=1 categorys_accuray[categories_name[label-1][1]]=categorys_true_count/categorys_img_count print(categorys_accuray) 123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627
结果:
{‘中药材’: 0.9878048780487805, ‘花生壳’: 1.0, ‘菌菇类’: 0.8901098901098901,
‘面包’: 0.6593406593406593, ‘核桃’: 1.0, ‘菜叶’: 0.8055555555555556,
‘菜根’:0.5409836065573771, ‘甘蔗皮’: 0.9761904761904762,
‘瓜子壳’:0.5106382978723404,‘饼干’: 0.9690721649484536}
面包、菜根、瓜子壳的准确率较低。下面将三种类别的真实边框与锚点进行可视化比较,如图 4 和图 5 所示。
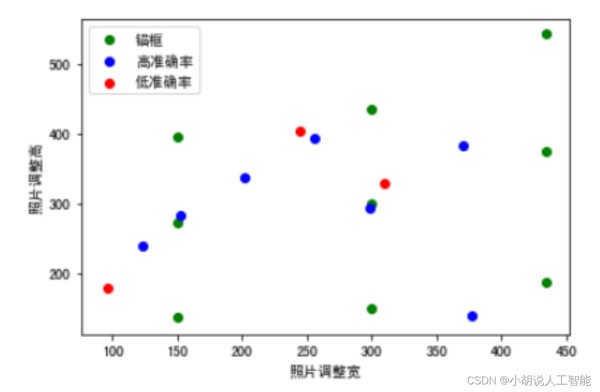
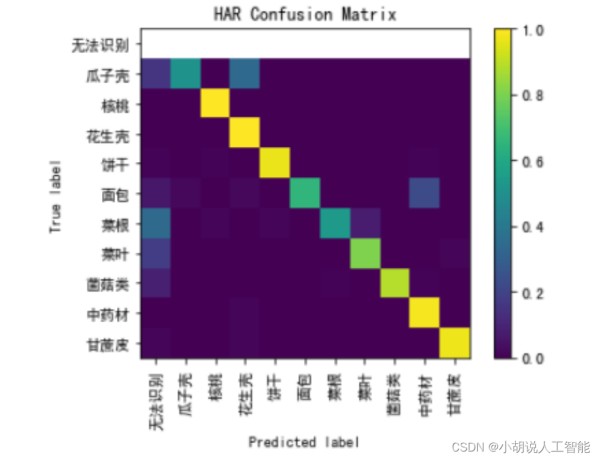
图 4 中可以看到左下角圆点,偏离较远,由参数知道此点为瓜子壳。偏离 anchor 较远的点容易出现无法识别的现象,例如瓜子壳、菜根等容易无法识别。图 5 中瓜子壳和花生壳容易混淆,面包和中药材容易混淆,菜根和菜叶容易混淆。正是由于无法识别混淆的情况,使得瓜子壳、菜根、面包准确率较低。
工程源代码下载
详见本人博客资源下载页
其它资料下载
如果大家想继续了解人工智能相关学习路线和知识体系,欢迎大家翻阅我的另外一篇博客《重磅 | 完备的人工智能AI 学习——基础知识学习路线,所有资料免关注免套路直接网盘下载》
这篇博客参考了Github知名开源平台,AI技术平台以及相关领域专家:Datawhale,ApacheCN,AI有道和黄海广博士等约有近100G相关资料,希望能帮助到所有小伙伴们。
网址:基于深度学习FasterRCNN模型Restnet50 的生活垃圾智能分类(准确率达84%) https://www.yuejiaxmz.com/news/view/736997
相关内容
基于深度学习的垃圾分类识别系统毕业设计:基于机器学习的生活垃圾智能分类系统
深度学习垃圾分类数据集
基于深度学习的生活垃圾检测与分类系统(网页版+YOLOv8/v7/v6/v5代码+训练数据集)
Python基于深度学习机器学习卷积神经网络实现垃圾分类垃圾识别系统(GoogLeNet,Resnet,DenseNet,MobileNet,EfficientNet,Shufflent)
基于机器视觉的垃圾自动分类系统设计
基于STM32的智能垃圾分类系统设计
【深度·聚焦】眉山开启智能回收新模式 引领生活垃圾分类新风尚
深圳:生活垃圾“分类收集减量+分流收运利用+全量焚烧处置”模式
基于深度学习模型的增强型智能家居控制与安防系统,Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing

