Android中的文件复制--视频和图片复制
public class FileOpreateUtils {
public static void copyfile(File fromFile, File toFile,Boolean rewrite ){
if(!fromFile.exists()){
return;
}
if(!fromFile.isFile()){
return;
}
if(!fromFile.canRead()){
return;
}
if(!toFile.getParentFile().exists()){
toFile.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
if(toFile.exists() && rewrite){
toFile.delete();
}
try {
FileInputStream fosfrom = new FileInputStream(fromFile);
FileOutputStream fosto = new FileOutputStream(toFile);
byte[] bt = new byte[1024];
int c;
while((c=fosfrom.read(bt)) > 0){
fosto.write(bt,0,c);
}
fosfrom.close();
fosto.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
不考虑多线程优化,单线程文件复制最快的方法是(文件越大该方法越有优势,一般比常用方法快30+%):
private static void nioTransferCopy(File source, File target) { FileChannel in = null; FileChannel out = null; FileInputStream inStream = null; FileOutputStream outStream = null; try { inStream = new FileInputStream(source); outStream = new FileOutputStream(target); in = inStream.getChannel(); out = outStream.getChannel(); in.transferTo(0, in.size(), out); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { close(inStream); close(in); close(outStream); close(out); } }如果需要监测复制进度,可以用第二快的方法(留意buffer的大小,对速度有很大影响):
private static void nioBufferCopy(File source, File target) { FileChannel in = null; FileChannel out = null; FileInputStream inStream = null; FileOutputStream outStream = null; try { inStream = new FileInputStream(source); outStream = new FileOutputStream(target); in = inStream.getChannel(); out = outStream.getChannel(); ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(4096); while (in.read(buffer) != -1) { buffer.flip(); out.write(buffer); buffer.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { close(inStream); close(in); close(outStream); close(out); } }常用的方法1是:
private static void customBufferBufferedStreamCopy(File source, File target) { InputStream fis = null; OutputStream fos = null; try { fis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(source)); fos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(target)); byte[] buf = new byte[4096]; int i; while ((i = fis.read(buf)) != -1) { fos.write(buf, 0, i); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { close(fis); close(fos); } }常用的方法2是:
private static void customBufferStreamCopy(File source, File target) { InputStream fis = null; OutputStream fos = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream(source); fos = new FileOutputStream(target); byte[] buf = new byte[4096]; int i; while ((i = fis.read(buf)) != -1) { fos.write(buf, 0, i); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { close(fis); close(fos); } }延伸:
在Java编程中,复制文件的方法有很多,而且经常要用到。我以前一直是缓冲输入输出流来实现的(绝大多数人都是如此),近来在研究JDK文档时发现,用文件通道(FileChannel)来实现文件复制竟然比用老方法快了近三分之一。下面我就来介绍一下如何用文件通道来实现文件复制,以及在效率上的对比
用文件通道的方式来进行文件复制
/**
* 使用文件通道的方式复制文件
*
* @param s
* 源文件
* @param t
* 复制到的新文件
*/
public void fileChannelCopy(File s, File t) {
FileInputStream fi = null;
FileOutputStream fo = null;
FileChannel in = null;
FileChannel out = null;
try {
fi = new FileInputStream(s);
fo = new FileOutputStream(t);
in = fi.getChannel();//得到对应的文件通道
out = fo.getChannel();//得到对应的文件通道
in.transferTo(0, in.size(), out);//连接两个通道,并且从in通道读取,然后写入out通道
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fi.close();
in.close();
fo.close();
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
与普通的缓冲输入输出流的复制效率的对比
普通的缓冲输入输出流代码:
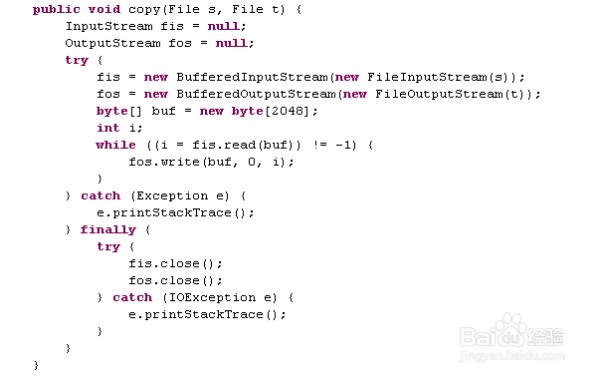
测试代码:
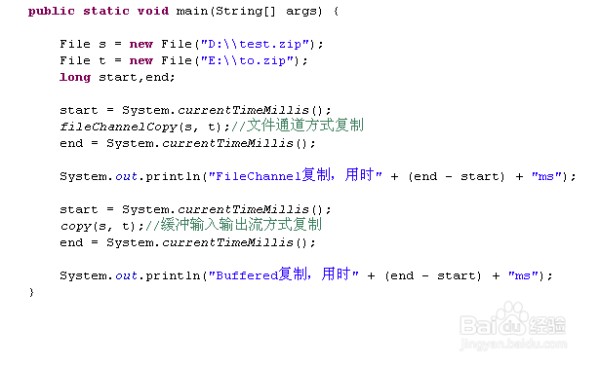
输出结果:
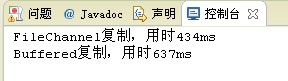

由此可见,FileChannel复制文件的速度比BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream复制文件的速度快了近三分之一。在复制大文件的时候更加体现出FileChannel的速度优势。而且FileChannel是多并发线程安全的。


