聚合物锂金属电池中的外部压力:评估循环性能时经常被忽视的标准?
自我管理能力、时间管理和压力管理也是生活质量评估中不可忽视的部分。 #生活乐趣# #生活质量# #生活质量改善# #生活质量评估工具#
摘要
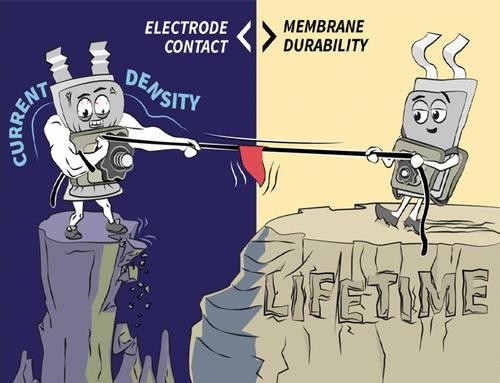
基于锂金属阳极、固体电解质和复合阴极的固态电池是实现高能量密度的一种前景广阔的电池概念。电池内的电荷载流子传输受制于固-固接触,这就强调了精心设计界面的重要性。增强电极活性材料和电解质之间界面接触的一个关键参数是对电池堆施加外部压力,尤其是在陶瓷电解质的情况下。然而,由于聚合物基电池总体上具有更好的润湿性,因此探讨外部压力对其影响的报告很少。在这项研究中,采用交联聚环氧乙烷(xPEO)和交联环糊精接枝聚己内酯(xGCD-PCL)评估了外部施加压力对关键性能指标的影响,包括电池寿命、速率能力和单层袋式 NMC622|| 锂电池的极限电流密度。值得注意的是,外部施加的压力会极大地改变电池的电化学循环性能,这在很大程度上取决于所考虑的聚合物的机械性能。较高的外部压力可能会增强电极-电解质界面,从而提高袋式电池的速率能力,尽管当聚合物电解质的塑性变形超过压缩应力的内在阈值时,电池的寿命可能会缩短。对于较软的 xGCD-PCL 膜,只有在没有外部压力的情况下才能进行电池循环,而对于 xPEO,在电池压力≤0.43 兆帕时就能实现速率能力增强和膜变形最小化之间的权衡,与采用陶瓷电解质的电池相比,外部压力≥5 兆帕要低得多,也更实用。
本文章由计算机程序翻译,如有差异,请以英文原文为准。
External Pressure in Polymer-Based Lithium Metal Batteries: An Often-Neglected Criterion When Evaluating Cycling Performance?
Solid-state batteries based on lithium metal anodes, solid electrolytes, and composite cathodes constitute a promising battery concept for achieving high energy density. Charge carrier transport within the cells is governed by solid–solid contacts, emphasizing the importance of well-designed interfaces. A key parameter for enhancing the interfacial contacts among electrode active materials and electrolytes comprises externally applied pressure onto the cell stack, particularly in the case of ceramic electrolytes. Reports exploring the impact of external pressure on polymer-based cells are, however, scarce due to overall better wetting behavior. In this work, the consequences of externally applied pressure in view of key performance indicators, including cell longevity, rate capability, and limiting current density in single-layer pouch-type NMC622||Li cells, are evaluated employing cross-linked poly(ethylene oxide), xPEO, and cross-linked cyclodextrin grafted poly(caprolactone), xGCD-PCL. Notably, externally applied pressure substantially changes the cell's electrochemical cycling performance, strongly depending on the mechanical properties of the considered polymers. Higher external pressure potentially enhances electrode–electrolyte interfaces, thereby boosting the rate capability of pouch-type cells, despite the fact that the cell longevity may be reduced upon plastic deformation of the polymer electrolytes when passing beyond intrinsic thresholds of compressive stress. For the softer xGCD-PCL membrane, cycling of cells is only feasible in the absence of external pressure, whereas in the case of xPEO, a trade-off between enhanced rate capability and minimal membrane deformation is achieved at cell pressures of ≤0.43 MPa, which is considerably lower and more practical compared to cells employing ceramic electrolytes with ≥5 MPa external pressure.
网址:聚合物锂金属电池中的外部压力:评估循环性能时经常被忽视的标准? https://www.yuejiaxmz.com/news/view/614247
相关内容
磷酸铁锂电池是如何维护的【钜大锂电】关于江西聚核锂电循环科技有限公司年利用5万吨退役锂电池资源循环项目环境影响报告书的拟批准公示
锂离子电池=微型炸弹?【钜大锂电】
丰田关于锂电池生命周期评价及回收再利用最新的研究与应用
基于浸没式液冷的锂电池热管理研究进展
锂电池短时充电,锂电池短时充电今日价格、行情走势、最新报价
北京一电动汽车电池爆炸,锂离子电池=定时炸弹?
格林美:公司回收再造的碳酸锂为电池级碳酸锂,碳酸锂的纯度超过99.6%,杂质含量低于行标电碳
太阳能发电板可以给锂电池充电吗
铁锂电池的“涅槃”:正极材料修复技术解析 在当今这个对能源效率和环境可持续性要求日益严格的时代,锂电池作为 新能源 的代表,其应用范围已经渗透到我们生活的方方面面...

