养老设施室外环境中4类重要空间的适老化设计 基于使用者的活动及需求
老龄化对环境的影响,如养老设施的建设与资源消耗,也是需要考虑的因素。 #生活知识# #社会生活# #人口老龄化#
摘要:
目的
近年来,中国人口老龄化程度不断加深且养老设施数量显著增加,然而养老设施室外环境设计往往忽略了使用者的真实需求,对养老设施室外环境展开深入研究具有很强的现实需求和紧迫性。
方法/过程
通过对国内外养老设施的实地调研,以及对设施内老年人、运营人员及来访亲友的深入访谈,了解其使用需求和对现有室外空间环境的评价,列举并总结出4类重要空间(集体活动广场、楼前活动场地、代际交流活动场地、认知症花园)主要使用者(老年人、护理人员)的活动特点及需求,并以此为出发点对空间设计中常见的问题进行分析。
结果/结论
结合实例,从运营实践和设计优化的角度对中国养老设施室外空间适老化环境建设中存在的问题进行研究探讨,针对4类重要空间提出具有可操作性的适老化设计要点,以期为未来养老设施项目的适老化设计提供指导,并为相关行业标准的制定提供参考。
Abstract:
Objective
In recent years, population aging has become increasingly deepening in China and the number of elderly care facilities has increased significantly. However, the outdoor environment design of elderly care facilities typically ignores the real needs of users. There is a strong practical demand and urgency for in-depth research on the outdoor environment of elderly care facilities.
Methods/process
Based on the field research on domestic and foreign elderly care facilities, and the interviews with the elderly living in elderly care facilities and their visiting relatives and friends as well as the operating personnel of such facilities, this research understands the facility usage requirements of these elderly people and their evaluation of the existing outdoor space environment. In addition, the research lists and summarizes the activity characteristics and needs of users (mainly the elderly and caregivers) of four types of important spaces (collective activity square; activity site in front of building; intergenerational activity site; garden for elderly people with dementia) and, on this basis, analyzes the common problems in space design.
Results/conclusion
Combined with examples, the research, from the perspective of design optimization and operation practice, studies and discusses some problems existing in the construction of elderly-oriented outdoor environment for elderly care facilities in China and, in view of the four types of important spaces mentioned above, proposes some feasible suggestions for elderly-oriented design, in hope of providing guidance for elderly-oriented design of future elderly care facility projects, and providing reference for the formulation of relevant industry standards.
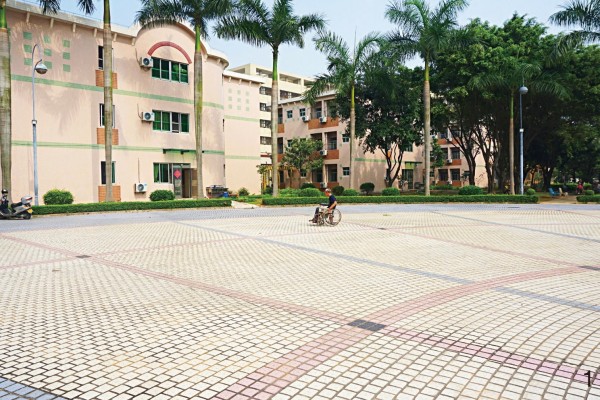

图 1 某养老设施中大而空旷的室外活动广场
Figure 1. A large and empty outdoor activity square in an elderly care facility
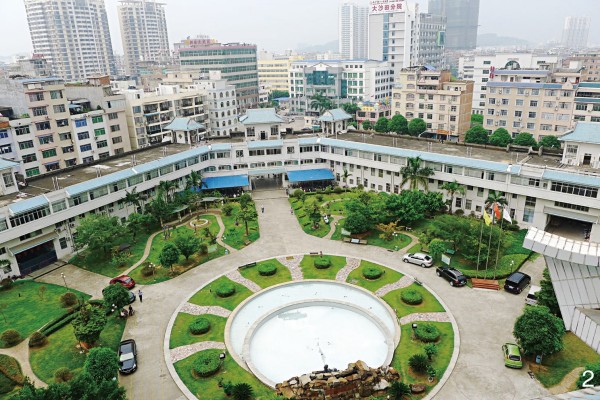

图 2 某养老设施中的景观布置影响了活动广场的完整性
Figure 2. The landscape layout of an elderly care facility affects the integrity of the activity square
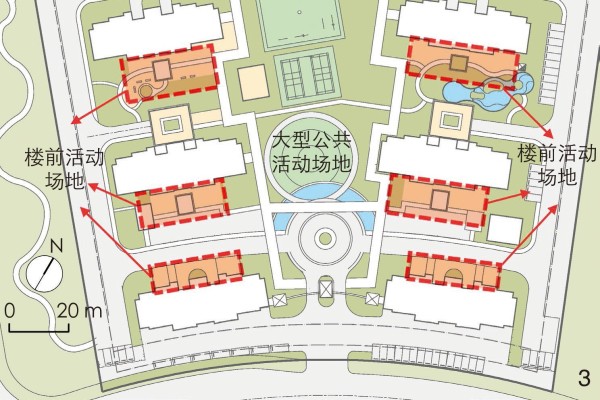
图 3 楼前活动场地位置示意
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the locations of activity sites in front of buildings
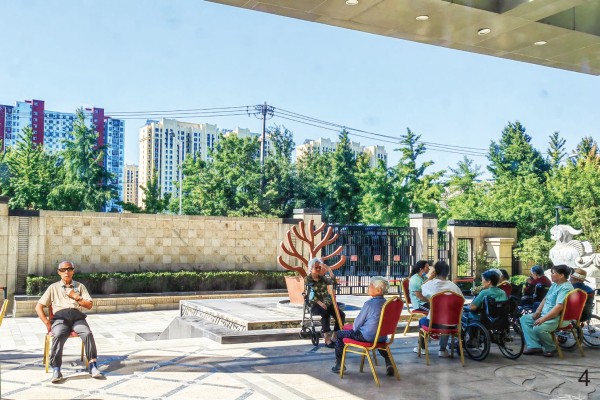

图 4 某养老设施中老年人在楼栋入口前休憩、交流
Figure 4. The elderly are relaxing and chatting in front of the building entrance in an elderly care facility
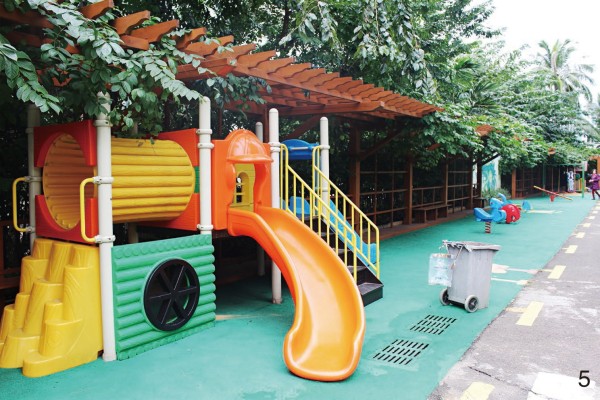

图 5 某养老设施中儿童活动游具被放置在角落,与其他活动场地缺乏联系
Figure 5. Children’s play equipment in an elderly care facility is placed in the corner, less connected with other activity sites in the facility
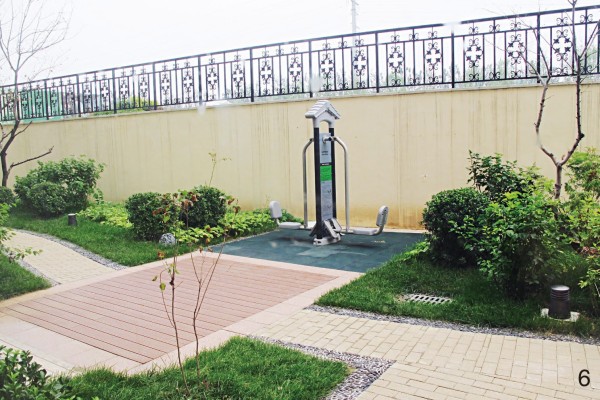

图 6 某养老设施中花园的围挡措施,容易让老人产生“被囚禁感”
Figure 6. The enclosure of the garden in an elderly care facility is easy to make the elderly feel “imprisoned”
图 7 结合采光、散步道、休息空间和周边植被等因素布置的活动广场
Figure 7. An activity square arranged in combination with such factors as lighting, walkway, rest space and surrounding vegetation
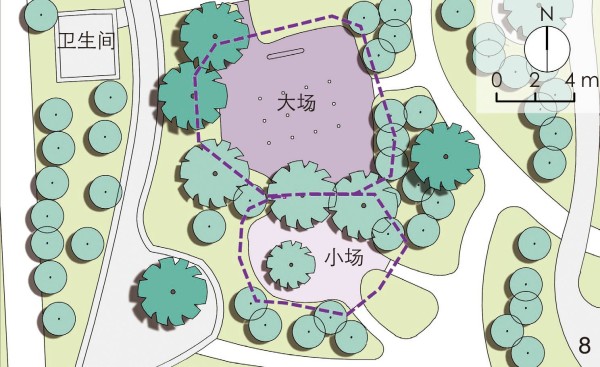
图 8 设置“大小场”,方便老年人“串场”开展多元活动
Figure 8. Set up “big and small squares” to facilitate the elderly’s participation in diversified activities

图 9 在活动场地周边布置可移动桌椅和伞架,有利于灵活调整休息区
Figure 9. Movable tables, chairs and umbrellas are arranged around the activity site, which is conducive to the flexible adjustment of the rest area

图 10 某养老设施中楼前活动场地设计实例(平面及实景图)
Figure 10. Design case of the activity site in front of building in an elderly care facility (plan and real view)
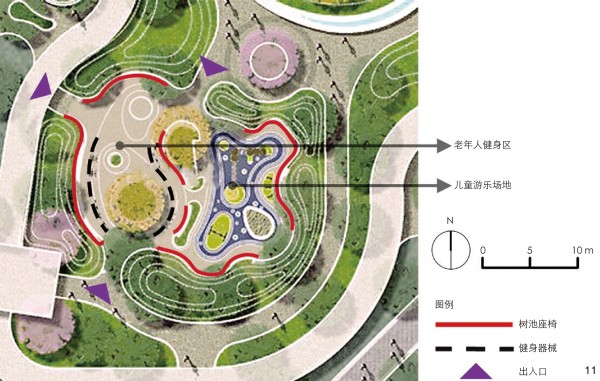
图 11 儿童活动场地与老年人健身区结合设置
Figure 11. The children’s activity area and the elderly fitness area are set together
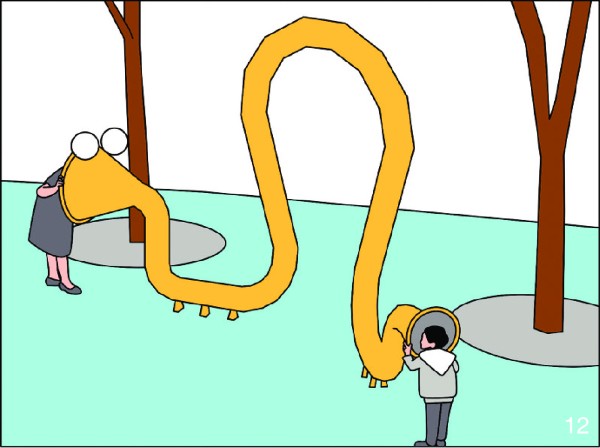
图 12 对话筒:老人和儿童可各站一侧通过传声互动
Figure 12. Speaking tube: the elderly and children can interact through sound transmission on each side of the tube
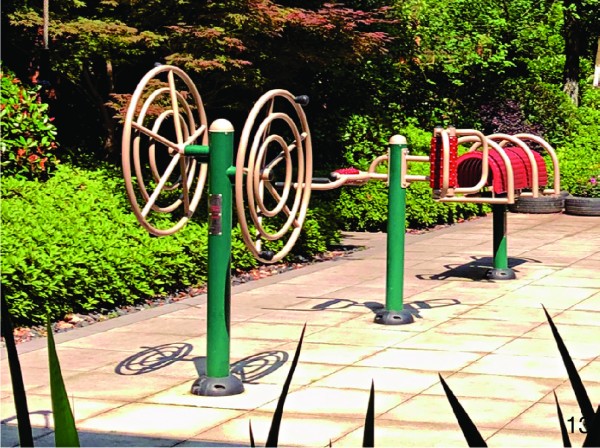

图 13 对面式转轮:老人和儿童可面对面使用、交流
Figure 13. Double shoulder joint trainer: the elderly and children can use and communicate face-to-face
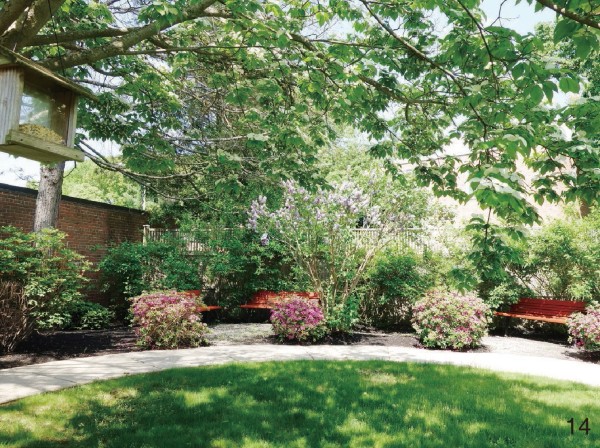

图 14 利用植物遮蔽围墙形成自然的花园边界,减少封闭感
Figure 14. Use plants to cover the enclosure to form a natural garden boundary and weaken the sense of closure
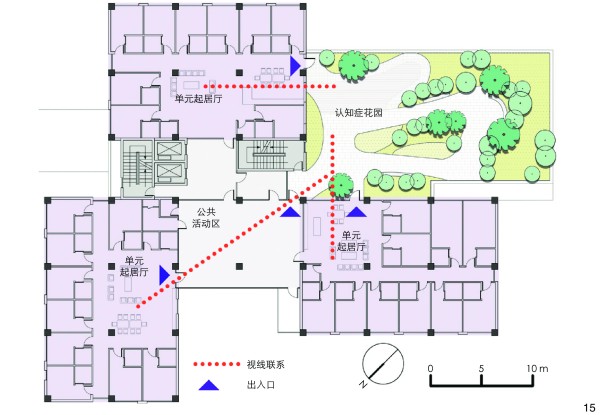
图 15 花园与单元起居厅有直接的视线联系,并可直接到达
Figure 15. The garden in an elderly care facility has direct line-of-sight contact with the living room of the units and can be reached directly
表 1 养老设施集体活动广场中的活动及需求
Table 1 Activities in and requirements for the collective activity square in elderly care facilities
活动使用者活动人数场地大小配置需求集体做操、跳舞等老年人、护理人员20~40做操/跳舞广场:150 m2左右;附属活动区、休息区等:50 m2左右需要完整的硬质铺装场地,周边配置较高大的
植被、景观种植区、特色景观雕塑等晒太阳、纳凉、赏景、
散步、交谈等10~20需要能够遮阴、挡雨的凉亭、廊架,带桌椅的
休息区,周边连接散步道、附属小型活动区等中秋节集会活动、重阳节
敬老/助老志愿活动等老年人、来访亲友、
运营人员、志愿者50需要可临时搭建的舞台、领操台或伞架等,并
配置用水点和卫生间
表 2 养老设施楼前活动场地中的活动及需求
Table 2 Activities in and requirements for the activity site in front of building in elderly care facilities
活动使用者活动人数场地大小配置需求晒太阳、纳凉、交谈、赏景、种植等老年人、护理人员3~5总面积约40~60 m2座椅、置物台、遮阳伞、亭子、景观花池、自理花池或菜园、1~2个健身器械等利用健身器械进行锻炼小规模的集体做操、跳舞、打太极等5~10含有完整硬质铺装的小场地表 3 养老设施代际交流活动场地中的活动及需求
Table 3 Activities in and requirements for the intergenerational activity site in elderly care facilities
活动使用者活动人数及场地大小配置需求儿童使用游具玩乐、在场地内奔跑,家长、老人照看儿童儿童、家长、老年人日常活动人数为5~10人,节假日有
儿童使用时人数会增多;
场地大小在50 m2左右供儿童玩乐的游具及器械、供老年人及家长休
息的桌椅、可停放轮椅及婴儿车的空间等老年人与孙辈在此交流、互动;其他老年人
(非亲属)在周边交谈、围观利于老幼互动的游具、器械(无儿童使用时)老年人在此进行常规的室
外运动,如散步、利用器械锻炼等老年人、护理人员部分空间或游具可多元利用,节假日供儿童使
用,平日供老年人活动使用
表 4 养老设施认知症花园中的活动及需求
Table 4 Activities in and requirements for the garden for elderly people with dementia in elderly care facilities
活动使用者及活动人数场地及配置需求其他管理需求康复练习、集体做操、跳舞、利用健身器械锻炼等使用者为认知症老人、护理人员;
活动人数在10人左右能满足约10人活动,有良好照明、通风的
独立院子;配置健身器械空间需封闭管理且视线无死角,尽可能消除围墙的“边界感”晒太阳、纳凉、交谈、赏景、种植等回游散步道、休息桌椅、自助花池、多元
植被景观及小品、小型动物饲养角等呆坐、反复徘徊、踱步等 [1] 国务院.国务院关于加快发展养老服务业的若干意见[EB/OL].(2013-09-13)[2023-01-31]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2013-09/13/content_7213.htm.
The State Council of PRC. Several Opinions of the State Council on Accelerating the Development of the Elderly Care Service Industry[EB/OL]. (2013-09-13)[2023-01-31]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2013-09/13/content_7213.htm.
[2] 民政部.2021年民政事业发展统计公报[EB/OL].(2022-08-26)[2023-01-31]. https://images3.mca.gov.cn/www2017/file/202208/2021mzsyfztjgb.pdf.Ministry of Public Security, PRC. 2021 Statistical Communiqué on the Development of Civil Affairs[EB/OL]. (2022-08-26)[2023-01-31]. https://images3.mca.gov.cn/www2017/file/202208/2021mzsyfztjgb.pdf.
[3] 李树华.尽早建立具有中国特色的园艺疗法学科体系(上)[J].中国园林,2000,16(3):15-17.LI S H. Call for Efforts to Establish the Horticultural Therapy Theory and Practice with Chinese Characteristic in the Near Future (Part One)[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2000,16 (3): 15-17.
[4]ULRICH R S. View Through a Window May Influence Recovery from Surgery[J]. Science,1984,224 (4647): 420-421. doi: 10.1126/science.6143402
[5]ULRICH R S. Effects of Gardens on Health Outcomes: Theory and Research[J]. Healing Gardens: Therapeutic Benefits and Design Recommendation, 1999, 27: 27-86.
[6]ULRICH R S. Effects of Healthcare Environmental Design on Medical Outcomes[C]//Design and Health: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Health and Design. Stockholm: Svensk Byggtjanst, 2001, 49-59.
[7]HAMILTON D K. The Four Levels of Evidence-Based Practice[J]. Healthcare Design,2003,3 (4): 18-26.
[8]HAMILTON D K, SHEPLEY M M. Design for Critical Care: An Evidence-Based Approach[M]. London: Routledge, 2010.
[9]RODIEK S D. A Missing Link: Can Enhanced Outdoor Space Improve Seniors Housing?[J]. Seniors Housing & Care Journal,2006 (14): 3-19.
[10]MOSCA E I. Design for All: Strategy to Achieve Inclusive and Healthier Environments[M]//Therapeutic Landscape Design: Methods, Design Strategies and New Scientific Approaches. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023: 113-125.
[11] 李树华.尽早建立具有中国特色的园艺疗法学科体系(下)[J].中国园林,2000,16(4):32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2000.04.012LI S H. Call for Efforts to Establish the Horticultural Therapy Theory and Practice with Chinese Characteristic in the Near Future (Part Two)[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2000,16 (4): 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6664.2000.04.012
[12] 李树华,黄秋韵.基于老人身心健康指标定量测量的园艺活动干预功效研究综述[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版),2020,50(6):852-866.LI S H,HUANG Q Y. A Review of Effects of Horticultural Intervention Based on Quantitative Measurements of Health and Well-Being of the Elderly[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2020,50 (6): 852-866.
[13] 李雪飞,黄秋韵,李树华,等.园艺植物栽培活动对失智老人身心健康的影响[J].西北大学学报(自然科学版),2020,50(6):867-880.LI X F,HUANG Q Y,LI S H,et al. Research on the Physical and Psychological Health Effect of the Horticultural Plant Cultivation Activity on the Elderly with Dementia[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2020,50 (6): 867-880.
[14] 李逸舟.感知体验下的老幼复合养老机构室外共享空间设计研究[D].北京: 北京工业大学, 2019.LI Y Z. Research on the Design of Outdoor Shared Space for Elderly and Young Compound Institutions Under Perceptual Experience[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2019.
[15] 刘博新,朱晓青.失智老人疗愈性庭园设计原则:目的、依据与策略[J].中国园林,2019,35(12):84-89. doi: 10.19775/j.cla.2019.12.0084LIU B X,ZHU X Q. The Principle of Healing Gardens Design for Elderly People with Dementia: Purpose,Basis and Strategy[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture,2019,35 (12): 84-89. doi: 10.19775/j.cla.2019.12.0084
[16]DAY K,CARREON D,STUMP C. The Therapeutic Design of Environments for People with Dementia: A Review of the Empirical Research[J]. The Gerontologist,2000,40 (4): 397-416. doi: 10.1093/geront/40.4.397
[17]FLEMING R,PURANDARE N. Long-Term Care for People with Dementia: Environmental Design Guidelines[J]. International Psychogeriatrics,2010,22 (7): 1084-1096. doi: 10.1017/S1041610210000438
[18] 李佳婧.失智养老设施的类型体系与空间模式研究[J].新建筑,2017(1):76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3959.2017.01.015LI J J. A Study on Type System and Spatial Mode of Dementia Care Facilities[J]. New Architecture,2017 (1): 76-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3959.2017.01.015
[19] 中国老龄协会.认知症老年人照护服务需求快速增长[EB/OL]. (2021-05-12) [2023-01-31]. http://www.cncaprc.gov.cn/llxw/192277.jhtml.China National Committee on Ageing. The Demand for Care Services for Elderly with Dementia is Growing Rapidly[EB/OL]. (2021-05-12)[2023-01-31]. http://www.cncaprc.gov.cn/llxw/192277.jhtml.
[20] 周燕珉.养老设施建筑设计详解3(上卷)[M].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2021.ZHOU Y M. Design and Interpretation of Elderly Care Facility III (Vol. 1)[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2021.
[21] 周燕珉.养老设施建筑设计详解3(下卷)[M].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2021.ZHOU Y M. Design and Interpretation of Elderly Care Facility III (Vol. 2)[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2021.
网址:养老设施室外环境中4类重要空间的适老化设计 基于使用者的活动及需求 https://www.yuejiaxmz.com/news/view/858066
相关内容
老年人需求下的居住区室外环境设计基于人本需求的老年家居生活环境设计
基于老年用户调查的社区养老模式下居住空间环境设计的研究
老年人室内环境的适老化设计
适老化理念的养老建筑空间设计
基于采光舒适度的典型养老设施阅读空间采光优化设计研究
舒适养老的家居及户外环境设计案例分享
居家适老环境设计重点
失智老人养老空间环境设计研究
基于智能化系统的空巢老人卧室环境设计研究

